Serial Dilution Advantages And Disadvantages

Dilution is the act of mixing a chemical with other substance, usually distilled water to make it lighter in composition. It is usually done if the chemical concentration is too high than the desired composition.
Serial Dilution Advantages And Disadvantages. 0 Comments Serial dilution is usually 1/10 dilution. Therefore after a series of dilutions, you have a logarithmic curve of concentration (log10). Basically, if diluting 1/10 and startin g off with 1 molar solution, first dilution = 0.1M, 2nd = 0.01M, 3rd = 0.001M. If making a 0.001M.
Thus, serial dilution simply means a series of repeated dilution performed on the same chemical basically to change its concentration. After performing the dilution, we need to know how much difference are the diluted chemical and the initial, undiluted ones. One way is by obtaining a factor called the Dilution Factor (DF). The factor can be obtained by dividing the actual volume of the initial chemical used to the final volume of the chemical after water is added.
As example, if 1.0 ml of 3M HCl is added with 9 ml of distilled water, the dilution factor becomes 1/10. In serial dilution, the entire dilution factor will be multiple together to be the actual dilution factor. There are several benefits of performing serial dilution. Serial dilution comes in handy when the solution is too concentrated to be used in experiments or ingredients preparation. This is to ensure that the exact concentration can be obtained for the experiment to become success. Other than that, the diluted solution from this serial dilution can be used to count the concentration of the actual solution. By knowing the dilution factor of certain solution, the calculations of the concentration become easier and systematic.
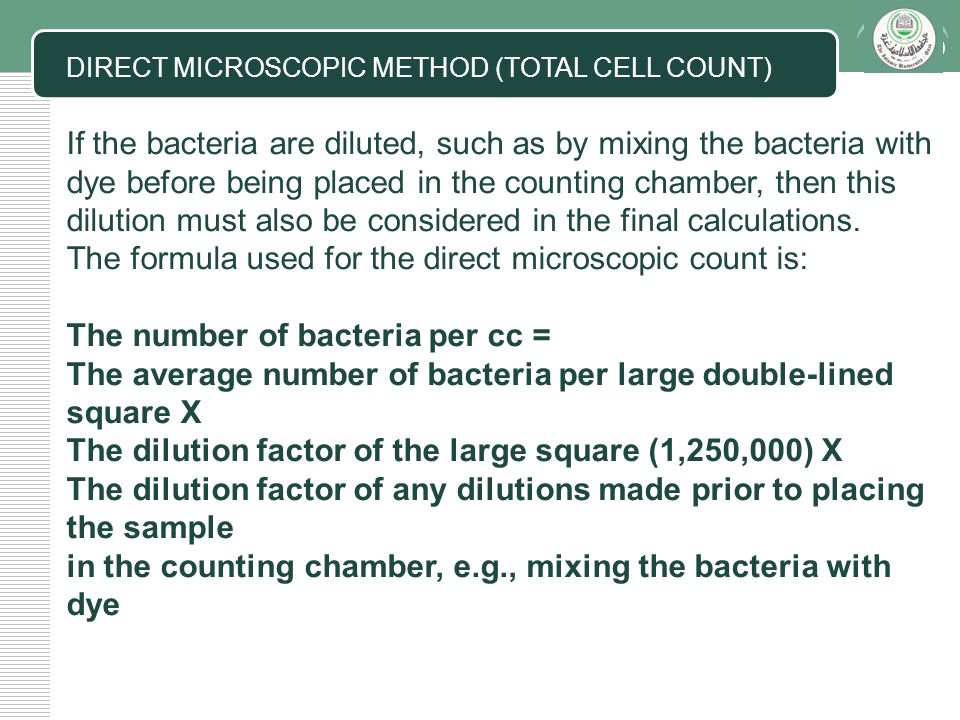
This method is applicable in several fields, not only in chemistry. Serial dilution is a simple yet efficient technique to determine the number of cells or organisms in a concentrated sample. Master kit ba8050 driver windows 7 download.
First, take a portion of the sample and does serial dilution on it. Repeat the steps until the cells can be observed under the microscope when the diluted sample was observed. Then, count the dilution factor and times it with the actual volume of the sample. Other than that, medicine administration require suitable dose for each patient with variable needs. This is where serial dilution is useful.
References 1. Colin Ratledge, Bjorn Kristiansen, Basic Biotechnology, Second Edition, (2001) Cambridge University Press. Bonifacino, Marry Dasso, Joe B.
Harford, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz and Kenneth M. Yamada, Short Protocols in Cell Biology: A Compendium of Methods from Current Protocols in Cell Biology, (2004), John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New Jersey. Aluizio Borem, Fabricio R. Santos and David E. Bowen, Understanding Biotechnology, (2003), Pearson Education, Inc.
- среда 27 марта
- 50